The National AI Centre (NAIC) is monitoring how small and medium enterprises (SMEs) use and view AI. We’re looking to understand how SMEs are adopting AI, the opportunities and challenges they face, and the value it brings to their businesses.
We’ve developed the AI Adoption Tracker for organisations working with SMEs to help accelerate their responsible AI journey.
You can explore trends and data through interactive dashboards on:
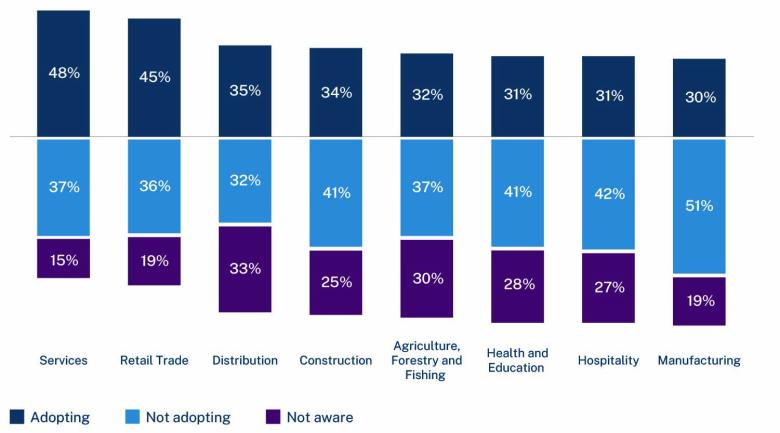
- AI adoption rates by business size, industry and location
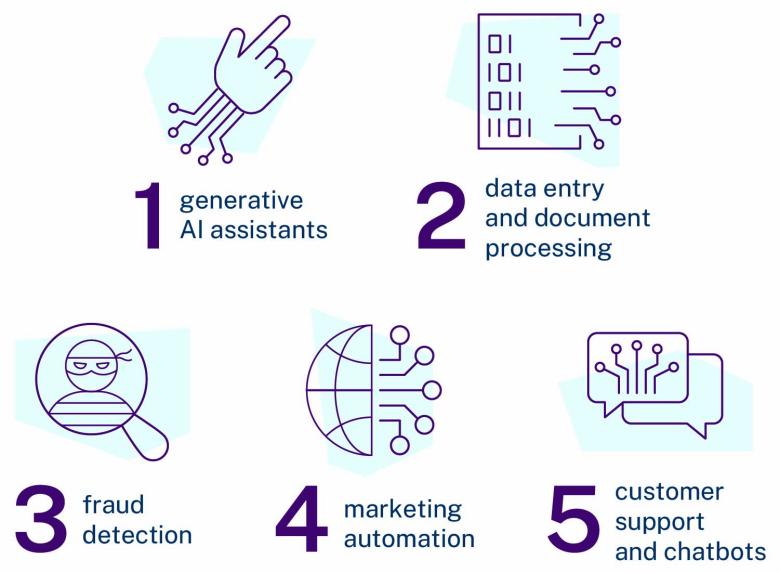
- awareness and use of different AI applications
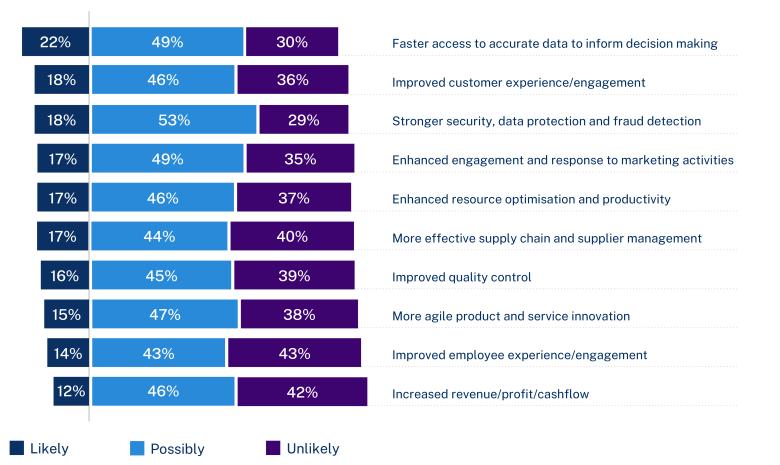
- perceived business outcomes, benefits and challenges.
We’re working with Fifth Quadrant on ongoing research to survey businesses, with 400 businesses responding each month. Our data starts from May 2024.
We’ll be updating data in the AI Adoption Tracker monthly and sharing quarterly insights about the main findings.
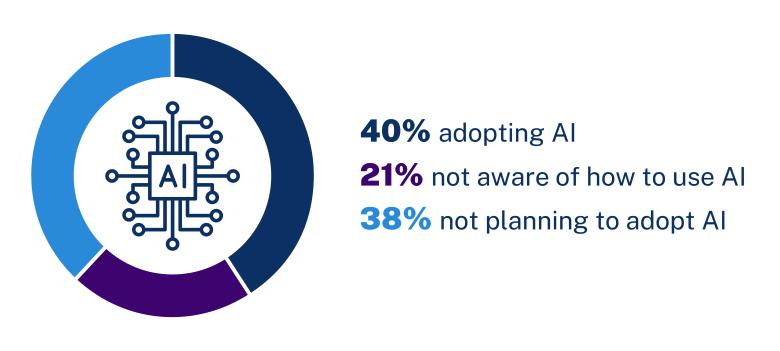
We’ve summarised findings for October to December 2024 below. We’ve rounded some statistics to make them easier to read.